Understanding how to value a restaurant involves a blend of art and science. The process requires analyzing various factors and using different methodologies (e.g., income approach, market approach, and/or cost approach) to determine a fair market value. This article delves into the key metrics, influencing factors, and current market trends that shape restaurant valuations.
Key Valuation Metrics
Restaurant valuation primarily revolves around two financial metrics: revenue and EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization). These metrics are crucial for applying valuation multiples, which can vary based on the restaurant type and prevailing market conditions.
- Revenue Multiples: This approach involves applying a multiple to the restaurant’s annual revenue. The multiple varies significantly depending on the restaurant’s growth prospects, profitability, market position, and overall economic conditions.
- EBITDA Multiples: EBITDA provides a clearer picture of the restaurant’s profitability by excluding non-operational expenses. This method is typically favored because it offers a normalized view of the business’s earning potential.
Factors Influencing Valuation Multiples
Several factors impact the valuation multiples of a restaurant:
- Brand Strength: Well-known and respected brands typically command higher multiples due to their established market presence and customer loyalty.
- Location: Prime locations significantly enhance a restaurant’s value by attracting more foot traffic and offering better market visibility.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficiently run operations with solid management teams can attract higher multiples.
- Growth Potential: Restaurants with significant growth opportunities through expansion or franchising are often valued higher.
- Economic Conditions: The broader economic environment is critical in determining valuation multiples. Favorable economic conditions generally lead to higher valuations.
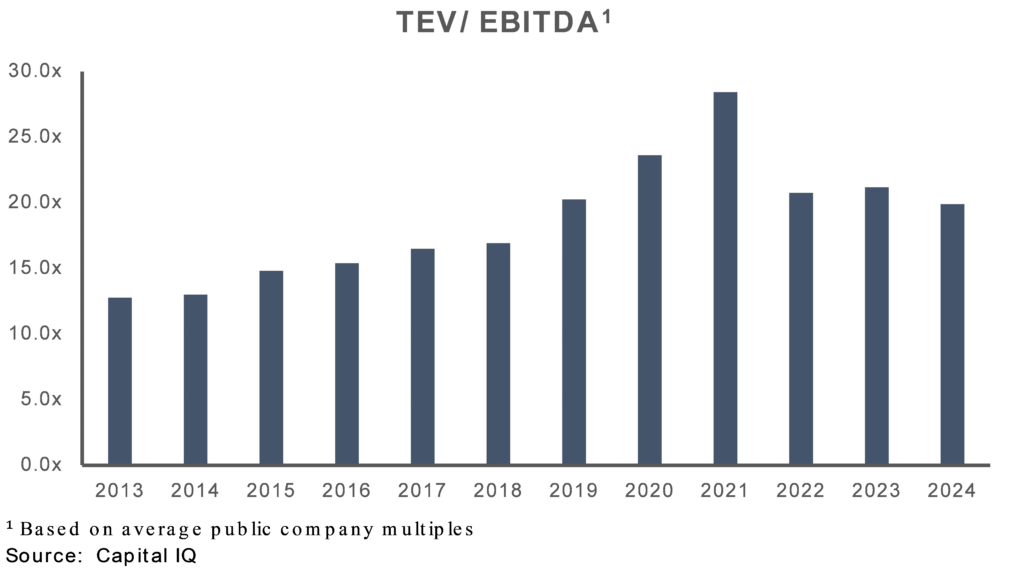
General Trends in EV/EBITDA Multiples (2013-2024)
The EV/EBITDA multiples for restaurants have varied over the past decade, influenced by broader economic conditions, sector-specific performance, and global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic. The multiples discussed below are averages of public companies; however, specific company multiples are based on risk factors specific to each company (e.g., smaller restaurants tend to transact at lower multiples due to the higher perceived risk). The multiples presented below simply aid in showing trends in the marketplace.
- 2013-2017: Steady Growth—The restaurant industry experienced steady growth in EV/EBITDA multiples. Strong consumer spending and economic recovery post-2008 financial crisis contributed to healthy valuations.
- 2017-2019: Peak Pre-COVID Valuations—This period saw elevated multiples due to robust economic conditions and strong financial performance in the restaurant sector.
- 2020: Impact of COVID-19—The pandemic significantly impacted the restaurant industry. Many businesses faced closures, reduced foot traffic, and operational challenges. Multiples during this time were highly segmented within the restaurant space, with fast-food chains and delivery-focused models showing better resilience. Also, note that valuations overall came down considerably during this time but at a slower rate than performance (resulting in temporarily elevated multiples)
- 2021: Recovery Phase—With the rollout of vaccines and easing restrictions, the restaurant industry began to recover, and multiples increased. In general, quick-service restaurants (QSRs) and pizza segments performed better during this period.
- 2022-2024: Stabilization and Growth—The industry saw stabilization with a focus on innovation, digital transformation, and changes in consumer behavior. Although transaction volumes have declined with increased financing costs and fewer quality acquisition targets, multiples have generally stabilized near 2019 levels, reflecting a more mature and adjusted market environment.
Current Merger & Acquisition Trends
Transaction activity slowed significantly in 2022 and the beginning of 2023 as sellers still hoped to receive the elevated multiples seen during 2021. Further, it has taken some time for the industry that has historically set valuation expectations based on a near-zero cost of capital to adjust to the new rate and return environment. The market for mergers and acquisitions improved during the last half of 2023 and is gaining momentum in 2024. While there is a flight to quality in the transactions that occur, buyers and sellers are coming together on valuations (e.g., fewer earnouts) as stores adjust to higher interest rates and lower profit margins.
Further, an increasing number of companies ending up on the market recently relate to distressed situations where thinning margins and higher interest rates push companies into insolvency, prompting increased fire sales as lenders look to recoup their investment.
Lastly, in the current environment, financing a transaction has become trickier. Banks are pickier in the transactions that are financed, terms are tougher, and the debt is more expensive. Often, the buyer puts more equity into their deals to get them across the finish line.
Conclusion
Over the past decade, EBITDA multiples for restaurants have fluctuated due to various economic and sector-specific factors. During the pandemic, valuation multiples were artificially high, but by 2022, multiples started to retreat to pre-pandemic levels.
Understanding these valuation multiples requires a comprehensive approach considering financial metrics, market conditions, and strategic growth opportunities. As the market evolves, staying attuned to economic trends, consumer preferences, and the role of private equity and M&A activities will be crucial for successfully navigating the restaurant valuation landscape in 2024 and beyond. Count on your GBQ team to stay on top of the trends.